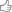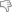-
Sylvhia.
User deleted
Gebel Barkal Pyramids
Gebel Barkal is a relief , on a large bend of the Nile, near the fourth cataract approximately 400 kilometers north of Khartoum, in Sudan. Historically it represents the maximum penetration of the Egyptian towards the south, in the Nubian territory, around 1450 BC, by the Egyptian Pharaoh Thutmose III. In this place the ruler founded the city of Napata that, about 300 years later, it became the capital of the independent kingdom of Kush.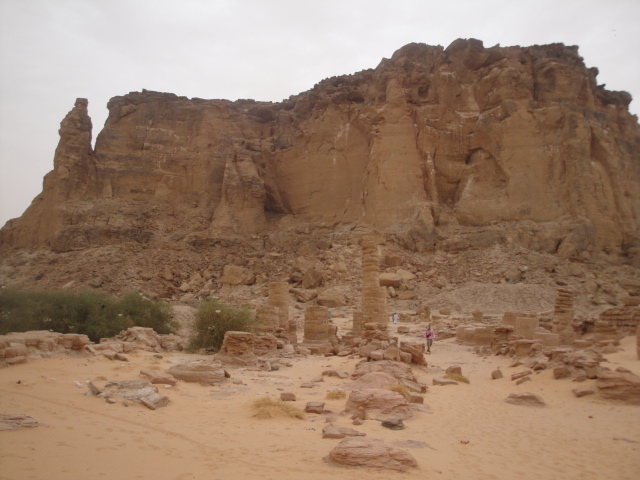 Credits : http://wanderingkraut.wordpress.com/
Credits : http://wanderingkraut.wordpress.com/
In this area of ancient Nubia, now Sudan territory, there are abundant archaeological remains that tell a glorious past. The ruins surrounding the Jabal Barkal include 13 temples and 3 palaces, described for the first time by European explorers in 1820, although only in 1916 were inaugurated the first archaeological excavations by George Reisner, an expedition sponsored by Harvard University and the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston. Since the seventies the explorations were carried out by a team from the University "La Sapienza" of Rome led by Sergio Donadoni, in collaboration with another team from the Boston Museum, in the eighties, following the latter by Timothy Kendall. The larger temples, such as that of Amon, are still considered sacred by local people.Potrait of George Reisner
The whole site is dominated by the Pure Mountain, in red sandstone with steep cliffs, which stands in the middle of a rather flat landscape crossed only by the path of the Nile. A sacred place, then, for a mountain that has always been considered sacred for this region of Nubia. To the north of the area stand out instead of the black rocks of the fourth cataract restricting the riverbed of the Nile watersAmon Temple
Near Jabal Barkal there was the ancient city of Napata, the center of the kingdom of Kush and Egypt itself during the XXV dynasty. Among the remains of relief, the Temple of Amon (XIX Dynasty Egyptian rebuilt by the rulers of the XXV dynasty) preceded by an avenue of rams that, in all probability, was to bring the pier Templar connected to the river. The interior rooms have been carved into the side of the mountain and are characterized by low reliefs and pillars on which is carved the figure of the god Bes. Splendid style columns hatoric that characterize the outer courtyard of the temple.Necropolis

Karima is one of the necropolis of Napata. A feature of this burial site are the Egyptian pyramids that differ from the model for the walls even more steep giving the structure a greater upward momentum, a pyramidal figure even more pointed and much less wide in the base. The necropolis is accompanied by that of nearby El Kurru and is in contrast to the real Nuri (21 burials of kings and 52 queens and princes) that is located on the opposite bank of the river, the east, built by King Taharqa (690 - 664 BC) and where it should be buried the same sovereign, although Sedeinga (much closer to the third cataract) you know another pyramid dedicated to him.
In contrast, the most ancient royal tombs are in the site of El Kurru. There it is possible to visit the burial chamber of Pharaoh Piankhi and that of a queen: typical inscriptions and frescoes in vibrant colors that respond to the dictates of Egyptian Nubian still not influenced by the taste.
Piankhi enlarged the Temple of Amun at Jabal Barkal and there laid his victory stela
http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gebel_Barkal.
Gebel Barkal Pyramids07 Settembre 2014 |