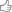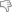-
Sylvhia.
User deleted
The Faroese Houses

The grass roofs are probably the first things you notice, and these have been a feature of the houses since the islands were first settled. In the Viking Age farmhouses had curved stone walls and the roof was supported by two rows of posts in a large common room with a longfire in the centre.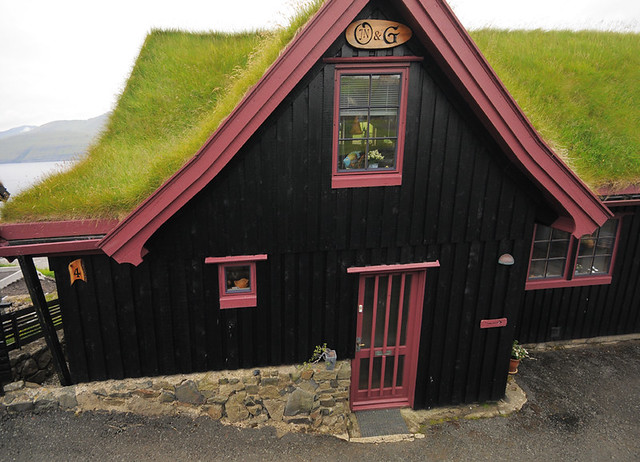
Along the outer walls benches or seats were placed, a Faroese home today is still called a sethús (seat house) after these seats. And there is a good reason that the ancient name has survived, for on the Faroes the original longhouse lasted longer than any other place in Scandinavia.
The house, with its protecting stone walls and the large grass roof, gradually developed into the traditional Faroese dwelling with the stall at one end, in the middle the smoke room with the working and sleeping areas, earth floor and the open fireplace with the louver in the roof as smoke outlet and light intake. At the other end of the house was the glass room, the farmer’s fine parlour with windows and jamb stove. Inside the smoke room and glass room there were vertical planks set in a groove between the posts and sills.
This is the same construction that was used in the historic Norwegian stave churches, but in tree rich Norway the stave constructed houses were gradually replaced by the shorter loghouses with horizontal logs. The stave constructions, which required less wood continued in the Faroes until the beginning of the twentieth century. Gradually the stonewalls were replaced by wood, except perhaps in the ends of the houses oriented against the fiercest wind direction. From this originated the classic Faroese house a low and small longhouse, tarred brown or black with white painted mullioned windows, blending into the terrain under a large grass roof.
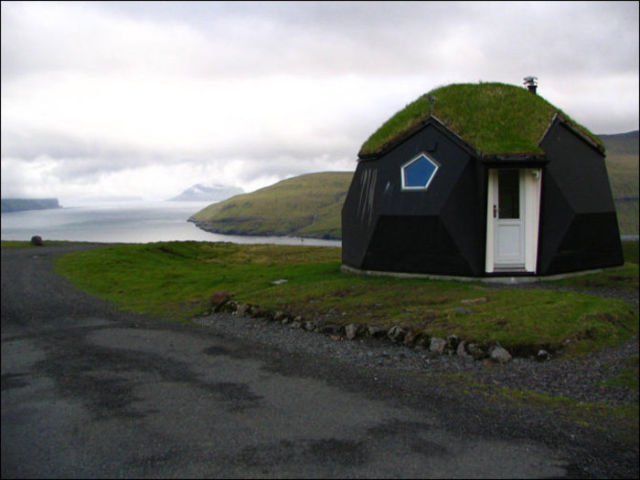


The churches were built in the same way. They were modest buildings, not much bigger than the other dwellings, but with a distinct difference: the little white bell tower, placed parallel or diagonally over the ridge of the roof. The inside of these churches are like chests made of untreated timber. All the designs are visible and simple, but every detail has its own special carving or image and the chancel wall, the half open wall between the nave and the choir, received the finest treatment.
Times changed and with the development of sea fishing new kinds of houses appeared. The longhouse was superseded by a more refined house on a high basement, and with dormers in the attic, but still tarred and with turfs of grass over a layer of beech bark. Then came fervent individualism, corrugated iron was placed as protection on the outside of wooden boards and together with the corrugated iron came paint in many colours. This colourful individualism has become respected through the years and even the authorities have supported it in later years, most directly in some experimental construction with individually built ter raced houses in the northern part of Tórshavn.
The painted roofs dominate, but you can still see new buildings with green grass. The most im portant of these is the Nordic House, where, as in the older dwellings, the roof lies over the house like a protecting wing and enhances the lines of the landscape. The grass still has something of a symbolic meaning and maybe it is a type of nostalgia when it is used on private houses. On the other hand it is a living material, which insulates and protects and requires very little aintenance. It also follows the beautiful seasons of the year and paints itself: brown in the autumn, white in the winter, burgeoning light green in the spring and lush green in the summer.



www.faroeislands.com/Default.aspx?pageid=10279.
The Faroese Houses |